Novel heterostructured Bi2S3/BiOI photocatalyst: facile preparation, characterization and visible light photocatalytic performance†
Abstract
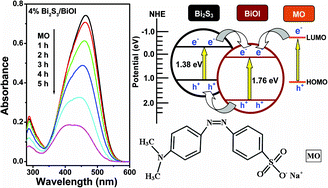
Novel Bi2S3/BiOI heterostructures were successfully synthesized through a facile and economical ion exchange method between BiOI and thioacetamide (CH3CSNH2), and characterized by multiform techniques, such as XRD, Raman, FT-IR, XPS, SEM, TEM, HRTEM, SAED, BET and DRS. The obtained Bi2S3/BiOI photocatalysts showed excellent photocatalytic performance for decomposing organic dye methyl orange (MO) compared with pure BiOI under visible light irradiation (λ > 420 nm). Among the Bi2S3/BiOI photocatalysts with different molar percentage of Bi2S3 to initial BiOI (from 2 to 8%), 4% Bi2S3/BiOI exhibited the highest photocatalytic activity with apparent kapp of 0.2968 h−1. Differently, Bi2S3/BiOI displayed low photocatalytic activity for many colorless organic substrates, such as phenol, 2-chlorophenol, dimethyl phthalate and 5-sulfosalicylic acid. Moreover, the study on the mechanism suggested that the enhanced photocatalytic activity mainly resulted from the role of Bi2S3–BiOI heterojunctions formed in the Bi2S3/BiOI, which could lead to efficient separation of photoinduced carriers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...