Synthesis, spectroscopic characterization, insulin-enhancment, and competitive DNA binding activity of a new Zn(ii) complex with a vitamin B6 derivative—a new fluorescence probe for Zn(ii)†
Abstract
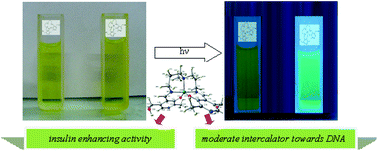
This paper describes the activity of a Schiff base ligand, derived from pyridoxal, as a promising fluorescence probe for biologically important Zn(II) ion sensing. This is the first report of a vitamin based ligand as a fluorescent probe for sensing Zn(II) ions. The Schiff base H2pydmedpt, derived from the condensation of pyridoxal (pyd) and N,N-bis[3-aminopropyl]methylamine (medpt), exhibits around a 325-fold increase in fluorescence quantum yield due to zinc triggered fluorescence switching. The response is specific for Zn(II) ions, and remains unaffected by the presence of alkali and alkaline earth metals but is suppressed to varying degrees by transition metal ions. The corresponding Zn(II)-complex, [Zn(pydmedpt], is isolated. The DFT optimized structure of the complex is compatible with elemental analysis, mass spectrometry, FT-IR, electronic and NMR spectra. The isolated complex, having pKa values of ∼5.3 and ∼5, is a moderate intercalator for DNA with an apparent binding constant of 2.3 × 106 M−1. The complex also shows insulin-enhancing activity at par with other reported complexes, with an IC50 value of 0.65 with respect to ZnSO4.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...