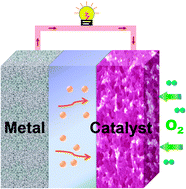
Because of the remarkably high theoretical energy output, metal–air batteries represent one class of promising power sources for applications in next-generation electronics, electrified transportation and energy storage of smart grids. The most prominent feature of a metal–air battery is the combination of a metal anode with high energy density and an air electrode with open structure to draw cathode active materials (i.e., oxygen) from air. In this critical review, we present the fundamentals and recent advances related to the fields of metal–air batteries, with a focus on the electrochemistry and materials chemistry of air electrodes. The battery electrochemistry and catalytic mechanism of oxygen reduction reactions are discussed on the basis of aqueous and organic electrolytes. Four groups of extensively studied catalysts for the cathode oxygen reduction/evolution are selectively surveyed from materials chemistry to electrode properties and battery application: Pt and Pt-based alloys (e.g., PtAu nanoparticles), carbonaceous materials (e.g., graphene nanosheets), transition-metal oxides (e.g., Mn-based spinels and perovskites), and inorganic–organic composites (e.g., metal macrocycle derivatives). The design and optimization of air-electrode structure are also outlined. Furthermore, remarks on the challenges and perspectives of research directions are proposed for further development of metal–air batteries (219 references).
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...