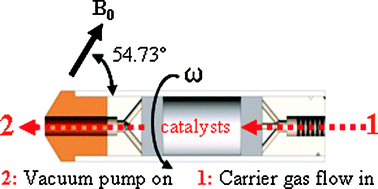
A large-sample-volume constant-flow magic angle sample spinning (CF-MAS) NMR probe is reported for in situ studies of the reaction dynamics, stable intermediates/transition states, and mechanisms of catalytic reactions. In our approach, the reactants are introduced into the catalyst bed using a fixed tube at one end of the MAS rotor while a second fixed tube, linked to a vacuum pump, is attached at the other end of the rotor. The pressure difference between both ends of the catalyst bed inside the sample cell space forces the reactants flowing through the catalyst bed, which improves the diffusion of the reactants and products. This design allows the use of a large sample volume for enhanced sensitivity and thus permitting in situ13C CF-MAS studies at natural abundance. As an example of application, we show that reactants, products and reaction transition states associated with the 2-butanol dehydration reaction over a mesoporous silicalite supported heteropoly acid catalyst (HPA/meso-silicalite-1) can all be detected in a single 13C CF-MAS NMR spectrum at natural abundance. Coke products can also be detected at natural 13C abundance and under the stopped flow condition. Furthermore, 1H CF-MAS NMR is used to identify the surface functional groups of HPA/meso-silicalite-1 under the condition of in situ drying. We also show that the reaction dynamics of 2-butanol dehydration using HPA/meso-silicalite-1 as a catalyst can be explored using 1H CF-MAS NMR.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...