Dynamic character of charge transport parameters in disordered organic semiconductor field-effect transistors
Abstract
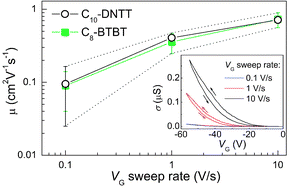
In this perspective article, we discuss the dynamic instability of charge carrier transport in a range of popular organic semiconductors. We observe that in many cases field-effect mobility, an important parameter used to characterize the performance of organic field-effect transistors (OFETs), strongly depends on the rate of the gate voltage sweep during the measurement. Some molecular systems are so dynamic that their nominal mobility can vary by more than one order of magnitude, depending on how fast the measurements are performed, making an assignment of a single mobility value to devices meaningless. It appears that dispersive transport in OFETs based on disordered semiconductors, those with a high density of localized trap states distributed over a wide energy range, is responsible for the gate voltage sweep rate dependence of nominal mobility. We compare such rate dependence in different materials and across different device architectures, including pristine and trap-dominated single-crystal OFETs, as well as solution-processed polycrystalline thin-film OFETs. The paramount significance given to a single mobility value in the organic electronics community and the practical importance of OFETs for applications thus suggest that such an issue, previously either overlooked or ignored, is in fact a very important point to consider when engaging in fundamental studies of charge carrier mobility in organic semiconductors or designing applied circuits with organic semiconductors.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Organic electronics - new physical chemistry insight

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...