Effect of ZnO nanofillers treated with triethoxy caprylylsilane on the isothermal and non-isothermal crystallization of poly(lactic acid)
Abstract
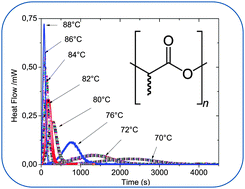
The crystallization of PLA–silane surface-treated ZnO nanocomposites was investigated by DSC and compared to that of neat PLA. Several modes of crystallization were considered: isothermal and non-isothermal cold crystallization and also isothermal and non-isothermal melt crystallization. The kinetics of cold crystallization were studied using different methods, namely the Avrami and Ozawa–Flynn–Wall models, to calculate activation energies and kinetic constants. In contrast to what is typically observed when the foreign particles are added in a polymer matrix, the silane surface-treated ZnO delayed the crystallization of PLA and made it more difficult to start. The nucleation activity of the ZnO nanoparticles, ϕ, was calculated and found to be greater than 1 (ϕ = 1.7). This indicated that ZnO played an anti-nucleating role in the crystallization of PLA nanocomposites. This effect has been linked mainly to the interactions between the silane groups onto the surface of nanoparticles and PLA macromolecules. These interactions which reduce the mobility of polymer chains have been evidenced by rheological experiments.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...