Photosensitizing properties of biopterin and its photoproducts using 2′-deoxyguanosine 5′-monophosphate as an oxidizable target†
Abstract
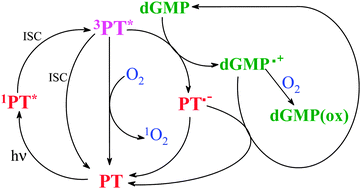
UV-A radiation (320–400 nm) induces damage to the DNA molecule and its components through photosensitized reactions. Biopterin (Bip) and its photoproducts 6-formylpterin (Fop) and 6-carboxypterin (Cap) accumulate in the skin of human beings suffering from vitiligo, a depigmentation disorder where the protection against UV radiation fails because of the lack of melanin. This study was aimed to evaluate the photosensitizing properties of oxidized pterins present in the skin and to elucidate the mechanisms involved in the photosensitized oxidation of purine nucleotides by pterins in vitro. For this purpose, steady-state and time-resolved experiments in acidic (pH 5.0–5.8) aqueous solution were performed using Bip, Fop and Cap as photosensitizers and the nucleotide 2′-deoxyguanosine 5′-monophosphate (dGMP) as an oxidizable target. The three pterin derivatives are able to photosensitize dGMP, being Fop the most efficient sensitizer. The reactions proceed through two competing pathways: (1) electron transfer from dGMP to triplet excited-state of pterins (type I mechanism) and (2) reaction of dGMP with 1O2 produced by pterins (type II mechanism). Kinetic analysis revealed that the electron transfer pathway is the main mechanism and the interaction of dGMP with the triplet excited-state of pterins and the formation of the corresponding dGMP radicals were demonstrated by laser flash photolysis experiments. The biological implications of the results obtained are also discussed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...