Isomerization mechanism of the HcRed fluorescent protein chromophore†
Abstract
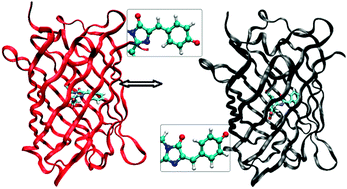
To understand how the
* Corresponding authors
a
Centre for Computational Molecular Science, Australian Institute for Bioengineering and Nanotechnology, The University of Queensland, Brisbane, Australia
E-mail:
q.sun@uq.edu.au
b Institute for Superconducting & Electronic Materials (ISEM), University of Wollongong, Wollongong, Australia
c
Max-Planck-Institut für Kohlenforschung, Kaiser-Wilhelm-Platz 1, D-45470 Mülheim an der Ruhr, Germany
E-mail:
thiel@mpi-muelheim.mpg.de
d Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Qingdao, P.R. China
e
University of Heidelberg, IWR, D-69120 Heidelberg, Germany
E-mail:
stefan.fischer@iwr.uni-heidelberg.de
f Facultad de Química Ambiental, Universidad Santo Tomás, Carrera 18 No. 9-27, Bucaramanga, Colombia
g Grupo de Bioquímica Teórica, Escuela de Química, Universidad Industrial de Santander, Carrera 27, Calle 9, Bucaramanga, Colombia
h
Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, USA
E-mail:
smithsc@ornl.gov
To understand how the

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Q. Sun, Z. Li, Z. Lan, C. Pfisterer, M. Doerr, S. Fischer, S. C. Smith and W. Thiel, Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012, 14, 11413 DOI: 10.1039/C2CP41217A
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
