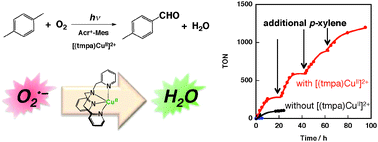
The catalytic durability of an organic photocatalyst, 9-mesityl-10-methyl acridinium ion (Acr+–Mes), has been dramatically improved by the addition of [{tris(2-pyridylmethyl)amine}CuII](ClO4)2 ([(tmpa)CuII]2+) in the photocatalytic oxygenation of p-xylene by molecular oxygen in acetonitrile. Such an improvement is not observed by the addition of Cu(ClO4)2 in the absence of organic ligands. The addition of [(tmpa)Cu]2+ in the reaction solution resulted in more than an 11 times higher turnover number (TON) compared with the TON obtained without [(tmpa)CuII]2+. In the photocatalytic oxygenation, a stoichiometric amount of H2O2 formation was observed in the absence of [(tmpa)CuII]2+, however, much less H2O2 formation was observed in the presence of [(tmpa)CuII]2+. The photocatalytic mechanism was investigated by laser flash photolysis measurements in order to detect intermediates. The reaction of O2˙− with [(tmpa)CuII]2+ monitored by UV-vis spectroscopy in propionitrile at 203 K suggested formation of [{(tmpa)CuII}2O2]2+, a transformation which is crucial for the overall 4-electron reduction of molecular O2 to water, and a key in the observed improvement in the catalytic durability of Acr+–Mes.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...