Oxidation mechanism of the intermetallic compound Ti3Al from ab initio thermodynamics
Abstract
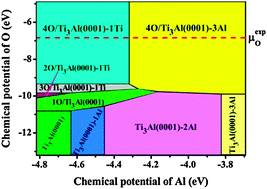
Ab initio density-functional theory and thermodynamics calculations are combined to establish a microscopic mechanism for the oxidation of the α2-Ti3Al(0001) surface. The surface energies as functions of the chemical potentials, as well as structural relaxations and electronic densities of states, are determined. The surface phase diagram (SPD) of the α2-Ti3Al(0001) systems with different defects and at various oxygen coverages is constructed. It is found that the Al antisite defect prefers to segregate on the α2-Ti3Al(0001) surface and oxygen

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...