Femtosecond fluorescence study of the reaction pathways and nature of the reactive S1 state of cis-stilbene
Abstract
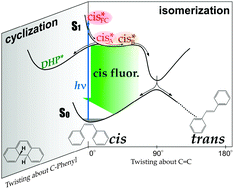
We report a femtosecond time-resolved fluorescence study of ![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C bond, while the second component is the fluorescence from the substantially twisted region around a shallow S1 potential minimum. The quantitative analysis of the femtosecond fluorescence data clearly showed that the whole isomerization process proceeds in the one-
C bond, while the second component is the fluorescence from the substantially twisted region around a shallow S1 potential minimum. The quantitative analysis of the femtosecond fluorescence data clearly showed that the whole isomerization process proceeds in the one-![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) C–Ph skeletal structure. On the basis of the results obtained, we discuss the dynamics and mechanism of the isomerization/cyclization reactions of
C–Ph skeletal structure. On the basis of the results obtained, we discuss the dynamics and mechanism of the isomerization/cyclization reactions of
- This article is part of the themed collection: Ultrafast chemical dynamics

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...