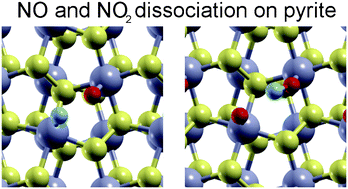
Sulphide materials, in particular MoS2, have recently received great attention from the surface science community due to their extraordinary catalytic properties. Interestingly, the chemical activity of iron pyrite (FeS2) (the most common sulphide mineral on Earth), and in particular its potential for catalytic applications, has not been investigated so thoroughly. In this study, we use density functional theory (DFT) to investigate the surface interactions of fundamental atmospheric components such as oxygen and nitrogen, and we have explored the adsorption and dissociation of nitrogen monoxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) on the FeS2(100) surface. Our results show that both those environmentally important NOx species chemisorb on the surface Fe sites, while the S sites are basically unreactive for all the molecular species considered in this study and even prevent NO2 adsorption onto one of the non-equivalent Fe–Fe bridge sites of the (1 × 1)–FeS2(100) surface. From the calculated high barrier for NO and NO2 direct dissociation on this surface, we can deduce that both nitrogen oxides species are adsorbed molecularly on pyrite surfaces.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...