Direct measurements of the high temperature rate constants of the reactions NCN + O, NCN + NCN, and NCN + M†
Abstract
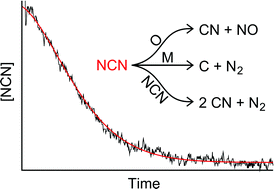
The rate constant of the reaction NCN + O has been directly measured for the first time. According to the revised Fenimore mechanism, which is initiated by the NCN forming reaction CH + N2 → NCN + H, this reaction plays a key role for prompt NOx formation in flames. NCN radicals and O atoms have been quantitatively generated by the pyrolysis of NCN3 and N2O, respectively. NCN concentration–time profiles have been monitored behind shock waves using narrow-bandwidth laser absorption at a wavelength of λ = 329.1302 nm. Whereas no pressure dependence was discernible at pressures between 709 mbar < p < 1861 mbar, a barely significant temperature dependence corresponding to an activation energy of 5.8 ± 6.0 kJ mol−1 was found. Overall, at temperatures of 1826 K < T < 2783 K, the rate constant can be expressed as kNCN + O = 9.6 × 1013 × exp(−5.8 kJ mol−1/RT) cm3 mol−1 s−1 (±40%). As a requirement for accurate high temperature rate constant measurements, a consistent NCN background mechanism has been derived from

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...