Morphology and growth mechanism of novel zinc oxide nanostructures synthesized by a carbon thermal evaporation process
Abstract
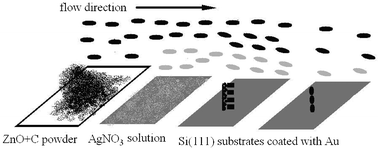
Two novel ZnO nanostructures were successfully synthesized using a carbon thermal evaporation process catalyzed by Au films and a AgNO3 solution, respectively. The morphologies were characterized in detail and show pendant necklace-shaped and bead necklace-shaped nanostructures. A new growth mechanism is stated to explain the growth of these two novel ZnO nanostructures. The decomposition of AgNO3 plays an important role and the polar H-bond, Ag–O, N–O and H–O bonds, as well as the oxygen resource, can affect the growth of the pendant necklace-shaped ZnO nanostructures. The bead necklace-shaped ZnO nanostructures were formed due to the Au catalyst.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...