Specific detection of DNA through coupling of a TaqMan assay with surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS)†‡
Abstract
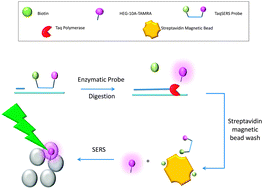
We have combined the benefits of a TaqMan assay with surface enhanced Raman scattering (
- This article is part of the themed collection: Emerging Investigators 2013

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...