Fused core particles as an alternative to fully porous sub-2 μm particles in pharmaceutical analysis using coupled columns at elevated temperature
Abstract
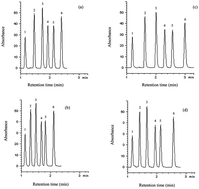
The chromatographic performance of columns packed with fused-core particles was compared to that of fully porous particles (sub-2 μm) at elevated temperature and extended column lengths. The study involved a comparison of chromatographic parameters such as retention, selectivity, resolution, efficiency and pressure drop. The analytes showed lower retention on fused core particles compared to sub-2 μm particles at low and high temperatures, with substantially lower backpressure. Van Deemter plots were constructed for both kinds of packing materials using single and coupled columns of different lengths at different temperatures. Lower backpressure across the fused core particles allowed two columns to be coupled at 30 °C to generate ∼66 000 theoretical plates, and three columns could be coupled at 60 °C generating ∼129 000 plates. On the other hand, only two sub-2 μm columns could be coupled at 60 °C generating ∼49 000 plates at the optimum flow rate. Fused-core particles showed similar efficiency to sub-2 μm particles at and below the optimum linear velocity, but with lower backpressure. As an application to

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...