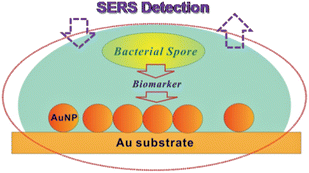
The development of ultrasensitive and rapid methods for the detection of bacterial spores is important for medical diagnostics of infectious diseases. While Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopic (SERS) techniques have been increasingly demonstrated for achieving this goal, a key challenge is the development of sensitive and stable SERS substrates or probes. This Minireview highlights recent progress in exploring metal nanoparticle-based substrates, especially gold nanoparticle-based substrates, for the detection of biomarkers released from bacterial spores. One recent example involves assemblies of gold nanoparticles on a gold substrate for the highly sensitive detection of dipicolinic acid (DPA), a biomarker for bacterial spores such as Bacillus anthracis. This type of substrate exploits a strong SERS effect produced by the particle–particle and particle–substrate plasmonic coupling. It is capable of accurate speciation of the biomarker but also selective detection under various reactive or non-reactive conditions. In the case of detecting Bacillus subtilis spores, the limit of detection is quite comparable (0.1 ppb for DPA, and 1.5 × 109 spores per L (or 2.5 × 10−14 M)) with those obtained using silver nanoparticle-based substrates. Implications of the recent findings for improving the gold nanoparticle-based SERS substrates with ultrahigh sensitivity for the detection of bacterial spores are also discussed.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...