Characterization of poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):tosylate conductive polymer microelectrodes for transmitter detection
Abstract
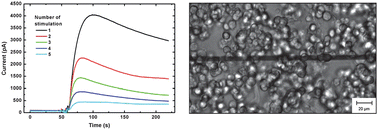
In this paper we investigate the physical and electrochemical properties of micropatterned poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):tosylate (PEDOT:tosylate) microelectrodes for neurochemical detection. PEDOT:tosylate is a promising conductive

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...