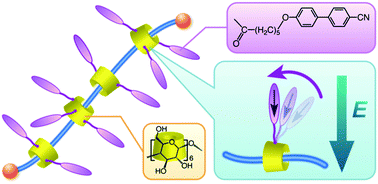
In this study, we have investigated molecular fluctuations in a liquid crystalline polyrotaxane (CB5PR) consisting of poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) and α-cyclodextrins (CDs) chemically modified with mesogenic cyanobiphenyl groups in solid state by dielectric spectroscopy. The results were compared with a hydroxypropylated polyrotaxane (HyPR) without mesogens. CB5PR showed a high-frequency relaxation mode, δ-relaxation due to the rotation of mesogenic groups at high temperature, whereas such a mode was not observed for HyPR. It was found that the activation energy of the rotational mode of mesogenic groups in CB5PR was considerably less than that in conventional side chain liquid crystalline polymers (LCPs). This indicated that the mesogenic groups around the polymer backbone in a solid-state PR rotated more easily than those in conventional LCPs, because mesogens bonded to cyclic CD in CB5PR can rotate independently of the rotational motion of the axis PEG. On the other hand, both CB5PR and HyPR exhibited broader relaxation processes at a much lower temperature around the glass transition of PEG, which was ascribable to the local molecular fluctuation of PEG. Our experimental results suggested that the local fluctuation of PEG in a PR was barely affected by the interaction between PEG and cyclic molecules, independently of the side chains around CD. This decoupling behavior is consistent with the low activation energy of the δ-relaxation in CB5PR.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...