A significant role of alkaline cations on the Reimer–Tiemann reaction†
Abstract
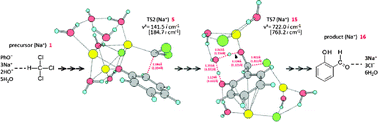
The Reimer–Tiemann (R–T) reaction was investigated by DFT calculations. A model composed of CHCl3, PhO−(Na+)H2O and [NaOH(H2O)2]2 was employed for geometry optimizations. A K+-containing model was also investigated. The dichlorocarbene reagent, which has been thought of for a long time, was found to intervene only transiently in the carbenoid form. In this form, the Na+ (or K+) coordination to CCl2 enhances its electrophilicity toward C6H5O−. The counter ion also works to stabilize the precursor phenoxide ion and intermediates of the substituted phenoxides in the hexagonal pyramidal coordination. The Na+-containing reaction consists of seven elementary processes, (K+, six ones) with extremely high exothermicity and spontaneity.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...