Synthesis of alanine-based colorimetric sensors and enantioselective recognition of aspartate and malate anions†
Abstract
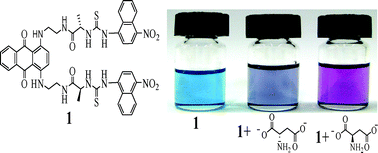
Two chiral colorimetric sensors (1,2) were synthesized and characterized by spectroscopic techniques and their enantioselective recognition of chiral dicarboxylic anions (D/

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...