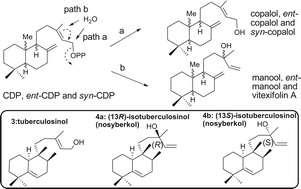
Substrate specificity of Rv3378c, an enzyme from Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and the inhibitory activity of the bicyclic diterpenoids against macrophagephagocytosis†
Abstract
The
* Corresponding authors
a
Department of Applied Biological Chemistry, Faculty of Agriculture and Graduate School of Science and Technology, Niigata University, Ikarashi 2-8050, Nishi-ku, Niigata, Japan
E-mail:
hoshitsu@agr.niigata-u.ac.jp
Fax: +81-25-262-6854
The

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
T. Hoshino, C. Nakano, T. Ootsuka, Y. Shinohara and T. Hara, Org. Biomol. Chem., 2011, 9, 2156 DOI: 10.1039/C0OB00884B
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
