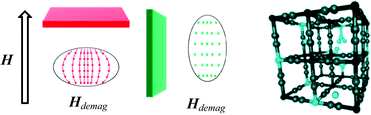
A series of Prussian blue analogue (PBA) thin films with thicknesses ranging from 25 nm to 2 μm and with the chemical formula RbjM1k[M2(CN)6]l·nH2O have been synthesized using sequential adsorption techniques (where M1 = Co2+, Ni2+, Cu2+, or Zn2+and M2 = Cr3+ or Fe3+). Since the resulting materials possess the PBA structure, changing the metal ions effectively tunes the magnetization density because SCo = 3/2, SNi = 1, SCu = 1/2, and SZn = 0 on the divalent metal sites and SCr = 3/2 and SFe = 1/2 on the trivalent metal sites. The effect of changing metal ions on the magnetic susceptibility, and specifically the difference between parallel and perpendicular orientations of the films with respect to the applied magnetic field, was investigated with SQUID magnetometry, and all samples, except the ZnFe PBA films, showed magnetic anisotropy. The films were also characterized with infrared spectroscopy, energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, atomic force microscopy, and scanning electron microscopy.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...