Preparation and electrochemical behaviors of composite solid polymer electrolytes based on polyethylene oxide with active inorganic–organic hybrid polyphosphazene nanotubes as fillers
Abstract
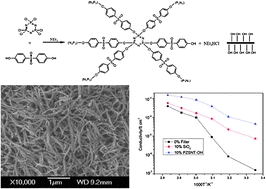
Inorganic–organic hybrid porous poly(cyclotriphosphazene-co-4,4′-sulfonyldiphenol) (PZS)

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...