Biodegradable cross-linked poly(amino alcoholesters) based on LMW PEI for gene delivery†
Abstract
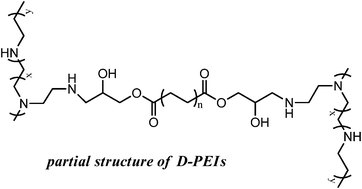
Polyethylenimine (
* Corresponding authors
a
Key Laboratory of Green Chemistry and Technology (Ministry of Education), College of Chemistry, and State Key Laboratory of Biotherapy, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610064, People's Republic of China
E-mail:
xqyu@scu.edu.cn, zwjulia@163.com
Fax: +862885415886
Tel: +86 28 85460576, +86 28 85164063
Polyethylenimine (

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
S. Li, Y. Wang, J. Zhang, W. Yang, Z. Dai, W. Zhu and X. Yu, Mol. BioSyst., 2011, 7, 1254 DOI: 10.1039/C0MB00339E
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
