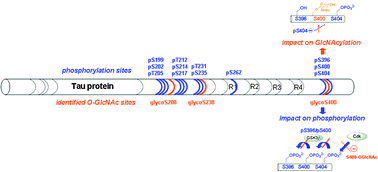
Identification of O-GlcNAc sites within peptides of the Tau protein and their impact on phosphorylation†
Abstract
* Corresponding authors
a
Unité de Glycobiologie Structurale et Fonctionnelle, CNRS UMR8576, IFR 147, Université de Lille1, 59655 Villeneuve d'Ascq Cedex, France
E-mail:
caroline.smet@univ-lille1.fr
Fax: +33 (0)3 2043 6555
Tel: +33 (0)3 2043 4997
b
Institut für Chemie und Biochemie, Freie Universität Berlin, Takustrasse 3, 14195 Berlin, Germany
E-mail:
hackenbe@chemie.fu-berlin.de
Fax: +49 (0)3 08385 2551
Tel: +49 (0)3083852451
c Miniaturisation pour l'Analyse, la Synthèse & la Protéomique, USR CNRS 3290, IFR 147, Université de Lille1, 59655 Villeneuve d'Ascq Cedex, France

 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
C. Smet-Nocca, M. Broncel, J. Wieruszeski, C. Tokarski, X. Hanoulle, A. Leroy, I. Landrieu, C. Rolando, G. Lippens and C. P. R. Hackenberger, Mol. BioSyst., 2011, 7, 1420 DOI: 10.1039/C0MB00337A
To request permission to reproduce material from this article, please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
If you are an author contributing to an RSC publication, you do not need to request permission provided correct acknowledgement is given.
If you are the author of this article, you do not need to request permission to reproduce figures and diagrams provided correct acknowledgement is given. If you want to reproduce the whole article in a third-party publication (excluding your thesis/dissertation for which permission is not required) please go to the Copyright Clearance Center request page.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content.
 Fetching data from CrossRef.
Fetching data from CrossRef.
This may take some time to load.
Loading related content
