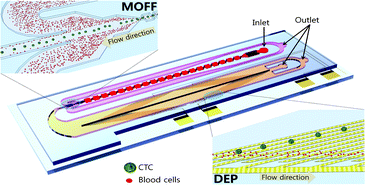
Continuous separation of breast cancer cells from blood samples using multi-orifice flow fractionation (MOFF) and dielectrophoresis (DEP)
Abstract
Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) are highly correlated with the invasive behavior of cancer, so their isolations and quantifications are important for biomedical applications such as cancer prognosis and measuring the responses to

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...