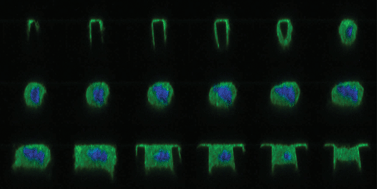
Most tissue cells evolve in vivo in a three-dimensional (3D) microenvironment including complex topographical patterns. Cells exert contractile forces to adhere and migrate through the extracellular matrix (ECM). Although cell mechanics has been extensively studied on 2D surfaces, there are too few approaches that give access to the traction forces that are exerted in 3D environments. Here, we describe an approach to measure dynamically the contractile forces exerted by fibroblasts while they spread within arrays of large flexible micropillars coated with ECM proteins. Contrary to very dense arrays of microposts, the density of the micropillars has been chosen to promote cell adhesion in between the pillars. Cells progressively impale onto the micropatterned substrate. They first adhere on the top of the pillars without applying any detectable forces. Then, they spread along the pillar sides, spanning between the elastic micropillars and applying large forces on the substrate. Interestingly, the architecture of the actin cytoskeleton and the adhesion complexes vary over time as cells pull on the pillars. In particular, we observed less stress fibers than for cells spread on flat surfaces. However, prominent actin stress fibers are observed at cell edges surrounding the micropillars. They generate increasing contractile forces during cell spreading. Cells treated with blebbistatin, a myosin II inhibitor, relax their internal tension, as observed by the release of pillar deformations. Moreover, cell spreading on pillars coated with ECM proteins only on their tops are not able to generate significant traction forces. Taken together, these findings highlight the dynamic relationship between cellular forces and acto-myosin contractility in 3D environments, the influence of cytoskeletal network mechanics on cell shape, as well as the importance of cell–ECM contact area in the generation of traction forces.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...