Co-precipitation synthesis of micro-sized spherical LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4 cathode material for lithium batteries
Abstract
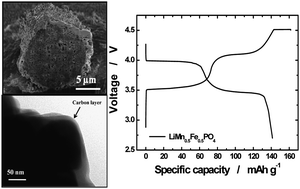
It is important to increase the energy density of olivine-type cathode materials utilizing micro-sized particles for rechargeable lithium batteries. However, according to the literature, micro-sized LiMn1−xFexPO4 compounds have limited specific capacity because they exhibit lower electrical conductivity than nano-sized materials: isolation of the inner part of the particles from the electrolyte results in an electrochemically inactive area during cycling, which hinders proper Li+ transport that causes the failure of the micron-sized particles. To improve the electrical conductivity of micro-sized LiMn1−xFexPO4, we designated micro-sized C-LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4 materials composed of nanopores in the micro-sized particles synthesized viaco-

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...