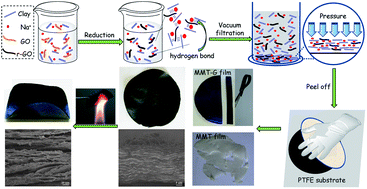
We report a simple and efficient method to fabricate flexible multifunctional free-standing montmorillonite-graphene (MMT-G) hybrid films viavacuum filtration. Aqueous colloidal dispersion of reduced graphene oxide (r-GO), stabilized by MMT nanoplatelets with variable content of r-GO, has been obtained by direct reduction of graphene oxide (GO) in the presence of exfoliated MMT nanoplatelets. The formation of stable dispersion of graphene sheets in water is a result from two contributing factors, i.e. the hydrogen-bonding interaction and the crosslinking effects originated from sodium ions acting as “crosslinkers” between r-GO sheets and MMT nanoplatelets. Through filtration, the two-dimensional and positively charged MMT and r-GO can self-assemble to form highly oriented hybrid films, where MMT and r-GO stack with each other in a fashion of interlocking arrangements. The MMT-G hybrid films thus obtained show excellent flexibility, electrical conductivity and fire-retardant properties. Therefore, it might be useful to further study and understand the non-covalent interactions between nanoclay and graphene in aqueous media, and open a new strategy for graphene applications in colloidal chemistry.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...