Graphene, carbon nanotube and ionic liquid mixtures: towards new quasi-solid state electrolytes for dye sensitised solar cells
Abstract
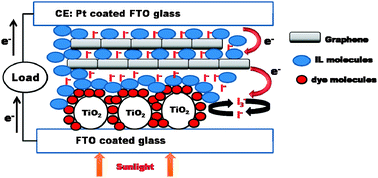
In this work carbon based nanomaterials in
- This article is part of the themed collection: Self-organisation of nanoparticles

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...