Light transmission from the large-area highly ordered epoxy conical pillar arrays and application to GaN-based light emitting diodes
Abstract
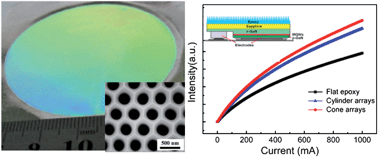
To improve the light transmission from the surface, we report a facile and cost-effective approach for the formation of wavelength-scale conical pillar arrays on a large surface area of epoxy resin. The highly ordered epoxy conical pillar arrays with a pitch of about 460 nm and height of about 800 nm have been successfully fabricated by the technique of shape-controlled

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...