Vacuum-assisted synthesis of graphene from thermal exfoliation and reduction of graphite oxide
Abstract
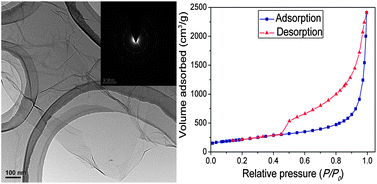
We report a vacuum-assisted method for thermal exfoliation and in situreduction of graphite oxide in large quantity at a temperature as low as 135 °C. The resulting

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...