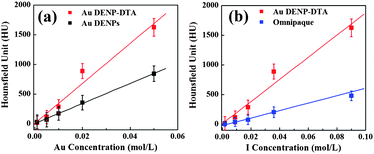
We describe a unique approach to combining two kinds of radiodense elements, gold and iodine, within one single dendrimer-based nanodevice with an enhanced X-ray attenuation property for potential computed tomography (CT) imaging applications. In this approach, amine-terminated generation 5 poly(amidoamine) dendrimers were used as templates for the entrapped synthesis of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs). The dendrimer-entrapped AuNPs (Au DENPs) were then conjugated with diatrizoic acid (DTA) via an EDC coupling reaction, resulting in the loading of 59 DTA molecules on average within each Au DENP nanodevice, where only 13 DTA molecules were covalently attached onto the surface of each dendrimer. The formed Au DENP–DTA nanocomplexes possessed a good stability in aqueous solution. X-ray absorption coefficient measurements reveal that the attenuation effect of Au DENP–DTA is much higher than that of both the commercial iodine-based contrast agent at the same iodine concentration and pure Au DENPs at the same gold concentration. With the prolonged circulation time of NPs, the Au DENP–DTA nanocomplex is expected to have a high efficacy as a contrast agent in dynamic CT imaging and angiography. This work demonstrates for the first time the enhancing effect of two different radiodense elements within the architecture of one contrast agent, presenting a novel concept for designing high-performance contrast agents for biomedical CT imaging applications.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...