Electrochemically assisted deposition on TiO2 scaffold for Tissue Engineering: an apatite bio-inspired crystallization pathway†
Abstract
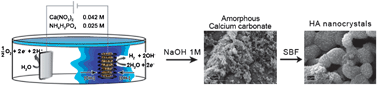
The interactions among inorganic materials and biological environments occurring at the nanoscale level are crucial to understand the mechanisms behind the bioactivity of biomaterials and for their better design. In the present study, we prepare TiO2 and TiO2/hydroxyapatite (HA) scaffolds for Tissue Engineering (

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...