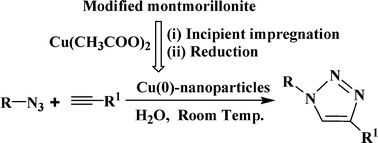
In situ generation of Cu(0)-nanoparticles in the nanopores of modified montmorillonite and their catalytic activity in 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition reactions between azides and terminal alkynes to synthesise 1,2,3-triazoles have been carried out. The modification of montmorillonite was carried out by activation with H2SO4 under controlled conditions for generating nanopores to act as a “host” for the Cu(0)-nanoparticles, which is executed by successful loading of Cu(CH3COO)2 metal precursor through an incipient wetness impregnation technique followed by reduction with NaBH4. A TEM study reveals that Cu(0)-nanoparticles within the size range of 0–10 nm are evenly distributed on the support. The synthesized Cu(0)-nanoparticles exhibit face centered cubic (fcc) lattice geometry and serve as an efficient green catalyst for the “Click” azide–alkyne cycloaddition to afford highly regioselective 1,4-disubstituted 1,2,3-triazoles with excellent yields and selectivity in aqueous medium. The nanocatalysts can be recycled and reused several times without significant loss of their catalytic activity.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...