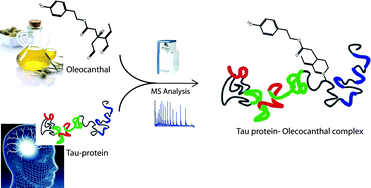
Oleocanthal (OLC) is a phenolic component of extra-virgin olive oil, recently supposed to be involved in the modulation of some human diseases, such as inflammation and Alzheimer. In particular, OLC has been shown to abrogate fibrillization of tau protein, one of the main causes of Alzheimer neurodegeneration. A recent interpretation of this mechanism has been attempted on the basis of OLC reactivity with the fibrillogenic tau hexapeptide VQIVYK and SDS-PAGE of OLC/tau incubation mixtures, suggesting that covalent modification events modulate tau fibrillization. In this paper we report a detailed mass spectrometric investigation of the OLC reactive profile with both tau protein fibrillogenic fragment K18 and propylamine in biomimetic conditions. We show that K18 is prone to be covalently modified by OLC through Schiff base formation between the ε-amino group of lysine residues and OLC aldehyde carbonyls. Moreover, as expected from its de-structured conformation, K18 shows a non-selective modification profile, reacting with several lysine residues to give cyclic pyridinium-like stable adducts. These data give new insights on the mechanism of inhibition of tau fibrillization mediated by OLC.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...