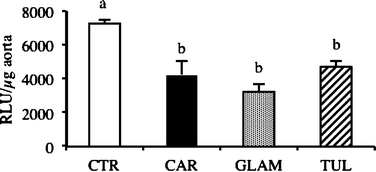
The effects of raspberries on early atherosclerosis in Syrian hamsters were investigated using three juices prepared from var. Cardinal, Glen Ample and Tulameen berries. The hamsters received an atherogenic diet for 12 weeks and at the same time a juice at a daily dose corresponding to the consumption of 275 ml by a 70 kg human. A control group received the same diet with water instead juice. The principal polyphenolic compounds in the juices were anthocyanins and ellagitannins, which were present at concentrations of 218–305 μg mL−1 and 45–72 μg mL−1, respectively. The three juices had similar but not identical effects. They all inhibited cardiac and aortic production of superoxide anion and increased hepatic glutathione peroxidase activity although only Tulameen juice brought about a significant increase in superoxide dismutase activity. Glen Ample was the only juice to significantly increase plasma paraoxonase activity. All the juices lowered plasma triglyceride level while consumption of Tulameen and Cardinal, but not Glen Ample, significantly lowered plasma total cholesterol and LDL-cholesterol. Cardinal was the sole juice to significantly increase HDL-cholesterol and likewise it also significantly reduced body weight. These findings suggest that moderate consumption of raspberry juices can help to prevent the development of early atherosclerosis, with the underlying mechanisms related to improved antioxidant status and serum lipid profiles.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...