An independent review and prioritization of past radionuclide and chemical releases from the Los Alamos National Laboratory – implications for future dose reconstruction studies
Abstract
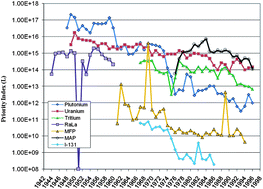
From 1999 through 2010, a team of scientists and engineers systematically reviewed approximately eight million classified and unclassified documents at Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL) that describe historical off-site releases of radionuclides and chemicals in order to determine the extent to which a full-scale dose reconstruction for releases is warranted and/or feasible. As a part of this effort, a relative ranking of historical airborne and waterborne radionuclide releases from LANL was established using priority index (PI) values that were calculated from estimated annual quantities released and the maximum allowable effluent concentrations according to The U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (USNRC). Chemical releases were ranked based on annual usage estimates and U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA) toxicity values. PI results for airborne radionuclides indicate that early plutonium operations were of most concern between 1948 and 1961, in 1967, and again from 1970 through 1973. Airborne releases of uranium were found to be of most interest for 1968, from 1974 through 1978, and again in 1996. Mixed fission products yielded the highest PI value for 1969. Mixed

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...