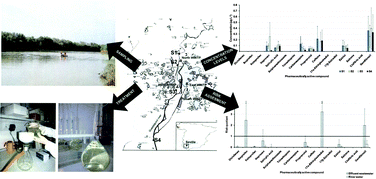
Guadalquivir River (South of Spain) is among the major freshwater sources of the European Atlantic basin. Until now scientific efforts have been focused on contamination by heavy metals and some priority pollutants in Guadalquivir River. However, the presence of “emerging contaminants”, such as pharmaceutically active compounds, has not yet been studied. In this work the occurrence and risk assessment of sixteen pharmaceutically active compounds, belonging to different therapeutic groups, in Guadalquivir River during its course through Seville city are reported. Wastewater effluents from four wastewater treatment plants discharging into Guadalquivir River and river water samples were analyzed. All studied pharmaceutically active compounds, except sulfamethoxazole, trimethoprim, estrone and clofibric acid, were detected in effluent wastewaters at concentration levels up to 28.9 μg L−1. Among the pharmaceutically active compounds found in effluent wastewater, seven were present in Guadalquivir River samples at concentration levels up to 0.75 μg L−1, which indicated an important dilution from effluent discharge. Environmental risk assessment reveals that potential ecotoxicological risk cannot be expected on Guadalquivir River at measured concentration levels. Only, the lipid regulator gemfibrozil showed a medium risk for the environment. The risk for acute toxic effects in the environment with the current use of active pharmaceutical ingredients is unlikely. However, the results do not rule out the potential for chronic environmental effects.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...