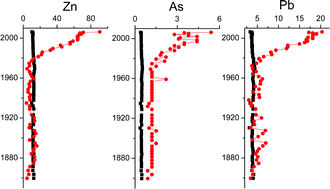
This paper presents the concentrations, vertical profiles and possible sources of selected major and trace elements in a sediment core covering ∼150 years of sedimentation in Lake Chaohu, eastern China. Element concentrations were measured by portable X-ray Fluorescence Spectroscopy (XRF) and were used to evaluate possible environmental consequences of the recent industrialization in China. Statistical analyses identify four groups: (1) organic carbon (OC), total nitrogen (TN), Pb, Zn, and As associated with the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides; (2) Mn, Cr, Ni and Cu from industrial and mining activities; (3) Fe, Rb, K, Co, Ti and Ca influenced by post-depositional processes and land exploitation; and (4) Zr and Sr from the soil. The vertical profiles of elements placed in the first two groups show distinct increases in concentrations above depths of 20 cm (∼1978), coincident with the timing of industrialization in China, and the anthropogenic-derived fluxes are higher than the lithogenic-derived fluxes over the last three decades. With the exception of Zr and Sr, association of the measured metals with organic carbon and nitrogen suggests that organic matter may act as a carrier phase. The geoaccumulation index (Igeo) reveals increased contamination from elements in the first two groups in recent years. Element concentrations, compared with the Effects Range-Low (ERL) and Effects Range-Median (ERM) levels set by NOAA, suggest that adverse biological effects from Ni contamination are very likely.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...