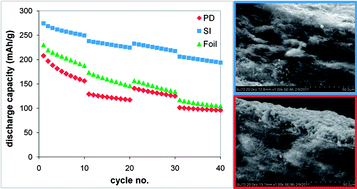
Lighter weight and longer life batteries for electrochemical energy storage are needed for many applications including aerospace, transportation, portable electronics, and biomedical devices. Inclusion of inert materials as part of the battery electrode significantly decreases energy density as they contribute to the weight and volume of the electrode, but not to its energy content. This work demonstrates the viability of using novel metal oxide/carbon nanotube substrate (CNT-S) electrodes in rechargeable cells. To our knowledge this is the first reported use of CNT-S for lithium battery cathodes without the use of a supporting metal current collector. Calculations show that the use of CNT-S can increase the cathode specific capacity by 20–60%, due to the low mass of the CNT-S and elimination of binders and other inert conductive carbons typically added to composite cathodes on foil current collectors. The oxidative stability of CNT-S relative to metal foil current collectors may extend battery lifetimes and enable use of electrolytes that are currently not viable. Two methods of preparing electrodes were demonstrated, the first using material deposited on the CNT substrate after isolation and the second method using direct integration during material synthesis.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...