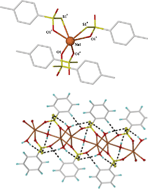
Three sodium thiosulfonate salts, NaMeS2O2·H2O, NaPhS2O2 and NaMeC6H4S2O2 have been prepared by the direct reaction of the sodium sulfinate salts with elemental sulfur, a clean, benign route that produces no by-products. The structures of the phenyl (which crystallised as a hydrate, NaPhS2O2·1.5H2O) and p-tolyl compounds were determined by X-ray crystallography. For the p-tolyl derivative, NaMeC6H4S2O2, the unexpected coordination of the pendant sulfur atom was found, a feature not reported previously for thiosulfonate salts, and observed only in two of the more common thiosulfate salts. Intermolecular CH/π interactions are postulated to contribute to the driving force of sulfur coordination, otherwise a different orientation of the aromatic rings would be expected. For NaPhS2O2·1.5H2O, the water ligands and thiosulfonate anions each contribute three oxygen atoms to form a NaO6 coordination sphere. The thiosulfonate and water oxygens bridge to other sodium atoms forming a three-dimensional layer structure consisting of sheets of NaPhS2O2·1.5H2O with a hydrophilic interior layer, comprising the sodium ions, water ligands and -S2O2−groups, and a hydrophobic exterior formed by the phenyl substituent. The structure is further stabilised by an extensive H-bonding network between the ligated water and the non-coordinating thiosulfonate sulfur atom forming part of the hydrophilic layer and by weak intermolecular edge-to-face CH/π interactions between the sheets. Investigation of the radical chemistry of the three salts using pulse radiolysis indicated that oxidation of NaMeS2O2·H2O involves formation of a sulfur-centred radical rather than hydrogen abstraction from the methyl substituent, whereas oxidation of the aromatic ring is the preferred pathway for the phenyl and p-tolyl derivatives.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...