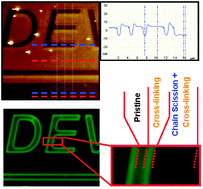
Irradiation damage, caused by the use of beams in the electron microscopes, leads to undesired physical/chemical material property changes or uncontrollable modification of structures that are being processed. Particularly, soft matter such as polymers or biological materials is highly susceptible and very much prone to react on irradiation by electron and ion beams. The effect is even higher when materials are subjected to energetic species such as ions that possess high momentum and relatively low mean path due to their mass. Especially when Ga+ ions (used as the ion source in Focused Ion Beam (FIB) instruments) are considered, the end-effect might even be the total loss of the material’s properties. This paper will discuss the possible types of degradation mechanisms and defect formations that can take place during ion and electron beam irradiation of the conjugated polymers: e.g. polyfluorene (PF) and poly-3-hexylthiophene (P3HT) thin films. For the investigation of the irradiation induced degradation mechanisms in this study, complementary analytical techniques such as Raman Spectroscopy (RS), Infrared Spectroscopy (IR), Electron Energy Loss Spectroscopy (EELS), Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM), and Fluorescence Microscopy including Photoluminescence (PL) and Electroluminescence (EL) Microscopy were applied.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...