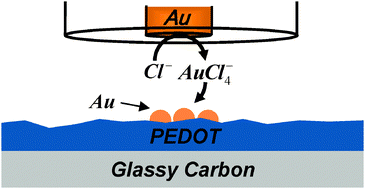
The deposition of Au and Ag, locally and from bulk solution, on poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) was studied. Specifically, PEDOT was electrochemically polymerized onto a glassy carbon (GC) electrode and used for bulk deposition of Au and Ag from their respective ions dissolved in the solution as well as for the local deposition of these metals using scanning electrochemical microscopy (SECM). These two sets of experiments were utilized to investigate the difference between Au and Ag electrochemical deposition on PEDOT. In particular, SECM experiments, which were conducted by the controlled anodic dissolution of Au and Ag microelectrodes close to GC/PEDOT, probed the effect of different PEDOT oxidation states on local deposition. The current–time transients recorded during the deposition, combined with scanning electron microscopy and EDX analysis provided insight into the reduction processes. AuCl4− and Ag+ ions were electrochemically reduced at a potential equal to and more negative than the ions redox potentials (0.4 and 0.2 V, respectively) and more positive than −0.7 V, where the PEDOT starts transforming into the reduced, i.e. insulating, state. We found that the electroreduction of Ag+ ions was diffusion-controlled and the PEDOT film served as a simple conductor. On the other hand, the reduction of AuCl4− ions was enhanced on GC/PEDOT as compared with bare GC, indicating that PEDOT catalyzes the reduction of AuCl4− to Au.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...