Applying the Z method to estimate temperatures of melting in structure II clathrate hydrates
Abstract
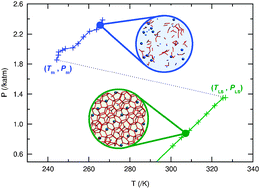
Equilibrium melting temperatures for structure II THF hydrate and argon/xenon (Ar/Xe) binary hydrate have been calculated using molecular dynamics using two melting techniques, namely the Z method [Belonoshko et al., Phys. Rev. B, 2006, 73, 012201] (applied for the first time to complex molecular solids) and direct phase coexistence simulations. The two methods give results in moderate agreement: calculations with the Z method give Tfus to be 250.7 K (0.77 katm) for THF and 244.3 K (1.86 katm) for Ar/Xe hydrate respectively; the corresponding direct phase coexistence calculations give Tfus in the range 235–240 K (0.77 katm) for THF and 240–252.5 K (1.86 katm) for Ar/Xe hydrate. The Z method was found to define the key thermodynamic states with high precision, although required long simulation times with these multicomponent molecular systems to ensure the complete melting required by the method. In contrast, the direct phase coexistence method did bracket the equilibrium temperature with little difficulty, but small thermodynamic driving forces close to phase equilibrium generated long-lived fluctuations, that obscured the precise value of phase coexistence conditions within the bracketed range.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Physics and chemistry of ice and water

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...