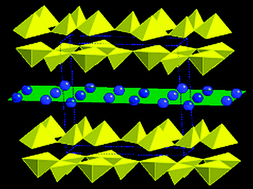
Sodium vanadium oxide gels, NaxV2O5·nH2O, of varying sodium content (0.12 < x < 0.32) were prepared by careful control of an ion exchange process. The water content (0.23 > n > 0.01) and interlayer spacing were found to be inversely proportional to the sodium level (x), thus control of sodium (x) content provided a direct, chimie douce approach for control of hydration level (n) and interlayer spacing, without the need for high temperature treatment to affect dehydration. Notably, the use of high temperatures to modify hydration levels can result in crystallization and collapse of the interlayer structure, highlighting the distinct advantage of our novel chimie douce synthesis strategy. Subsequent to synthesis and characterization, results from an electrochemical study of a series of NaxV2O5·nH2O samples highlight the significant impact of interlayer water on delivered capacity of the layered materials. Specifically, the sodium vanadium oxide gels with higher sodium content and lower water content provided higher capacities in lithium based cells, where capacity delivered to 2.0 V under C/20 discharge ranged from 170 mAh/g for Na0.12V2O5·0.23H2O to 300 mAh/g for Na0.32V2O5·0.01H2O. The capacity differences were maintained as the cells were cycled.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...