Metal flux through consuming interfaces in ligand mixtures: boundary conditions do not influence the lability and relative contributions of metal species†
Abstract
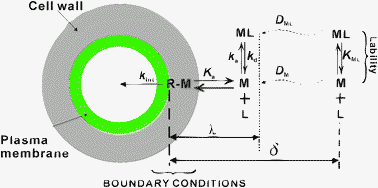
In a mixture of metal ions and complexes, it is difficult to predict ecological risk without understanding the contribution of each metal species to biouptake. For microorganisms, the rate of uptake (internalization flux) has not only a major influence on the total metal flux but also on the bioavailability of the various metal species and their relative contributions to the total flux. In this paper, the microorganism is considered as a consuming interface, which interacts with the metal ion, M, via the Michaelis–Menten boundary conditions. The contribution of each metal complex to the overall metal flux, in relation to its lability, is examined for a number of important boundary parameters (the equilibrium constant Ka of metal with transport sites, internalization rate constant kint and total transport sites concentration {R}t). Computations were performed for Cu(II) complexes, in a multicomponent culture medium for microoganisms. For a one-ligand system, results were acquired using rigorous mathematical expressions, whereas approximate expressions, based on the reaction layer approximation (RLA) and rigorous numerical computations (computer codes MHEDYN and FLUXY), were employed for

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...