Mechanism of oxygen reactions at porous oxideelectrodes. Part 2—Oxygen evolution at RuO2, IrO2 and IrxRu1−xO2electrodes in aqueous acid and alkaline solution†‡
Abstract
The kinetics and mechanism of the
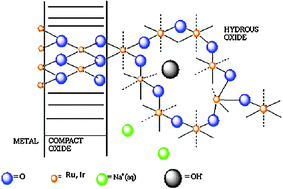
- This article is part of the themed collection: Interfacial processes and mechanisms

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...