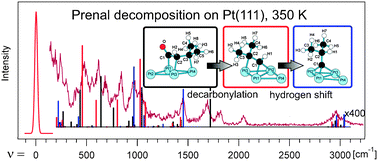
The prediction of a reaction mechanism and the identification of the corresponding chemical intermediates is a major challenge in surface science and heterogeneous catalysis, due to a complex network of elementary steps and surface species. Here we demonstrate how to overcome this difficulty by tracking the temperature dependent formation of the initial reaction intermediates and identifying the decomposition pathways in the case of prenal, an α,β-unsaturated aldehyde, on the Pt(111) model catalyst surface by combining vibrational spectroscopy, thermal reaction/desorption spectroscopy (TPRS) experiments and detailed theoretical analysis. TPRS characterization of this reaction up to 600 K shows a series of desorption states of H2 (∼280 K, 410 K and 473 K) and CO (∼414 K), giving valuable insights into the sequence of elementary steps suggesting that the loss of hydrogen and the carbonyl functions are among the first elementary steps. HREELS experiments recorded after annealing to specific temperatures result in complex spectra, which can be assigned to several subsequently formed and transformed surface intermediates. Starting from stable prenal adsorption structures, complementary DFT calculations allow the determination of the most likely reaction pathway for the initial decomposition steps and the identification of the corresponding intermediates by comparison with HREELS. The decomposition occurs from the strongly bonded prenal adsorption structures via a dehydro-η3-triσ(CCC)-H1 intermediate to the highly stable η1-isobutylidyne species at high temperatures.
You have access to this article
 Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?
Please wait while we load your content...
Something went wrong. Try again?


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...